Do you know what a fulvic acid is? It is an essential component in the agricultural field. In today’s Artal article, we will talk about this acid.
We will answer what it is, what is its practical use in agriculture and what are the specific properties that distinguish it.
Additionally, we will compare the fundamental differences between humic and fulvic acids.
And if you want to use these acids in your soils and fields, we will present you Fertiorgan Humus, an innovative product from Artal that capitalizes on the advantages of fulvic acid to boost crop performance and sustainability.

What is a fulvic acid
First of all, let’s define what it is. Fulvic acid is a natural organic component present in soil, formed by the decomposition of organic matter such as plants and microorganisms.
It is characterized by its complex molecular structure and its unique ability to chelate minerals, which facilitates their absorption by plants.
This acid plays a crucial role in improving soil structure, water retention and nutrient release, thus promoting plant growth and health.
In addition, it acts as a powerful chelating agent, helping the solubilization and transport of essential nutrients to the roots of plants.
As for fulvic acid for human consumption, research is in its early stages.

What is it for
And what is fulvic acid used for? It plays multiple beneficial roles in agriculture and plant nutrition.
Firstly, it acts as a chelating agent, helping to solubilize and transport essential nutrients to the roots, facilitating their absorption by plants.
In addition, it improves the structure of the soil, increasing its capacity to retain water and nutrients, which promotes healthy root development and plant resistance to water stress.
It can also stimulate microbial activity in the soil, promoting the decomposition of organic matter and the release of nutrients.
Another function is to help balance a soil that tends to be too acidic, helping to create more alkaline or neutral soils to favor the development of crops.

Properties of fulvic acid
In this section, we will explain the properties and benefits of fulvic acid:
- Improves soil structure. It helps to increase the aggregation of soil particles, improving its structure and porosity. This favors water and nutrient retention, as well as soil permeability.
- Increases the nutrients’ absorption. It acts as a chelating agent, forming complexes with nutrients such as iron, calcium and magnesium, which facilitates their absorption by plants. This optimizes the availability of essential nutrients for the growth and development of crops.
- Stimulates plant growth. It promotes root growth, seed germination and shoot development, which results in more vigorous plants that are resistant to environmental stress.
- Increases microbial activity. It promotes the activity of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, which improves the decomposition of organic matter and the mineralization of nutrients, multiplying the availability of nutrients for plants.
- Strengthens tolerance to abiotic stress. It helps reduce their negative effects, such as drought, salinity and extreme temperatures, by improving the ability of plants to absorb and use water and nutrients.
- Increases the quality of crops. The use of fulvic acid can result in superior quality crops, with better flavor, texture and nutritional content, as well as greater resistance to diseases and pests.
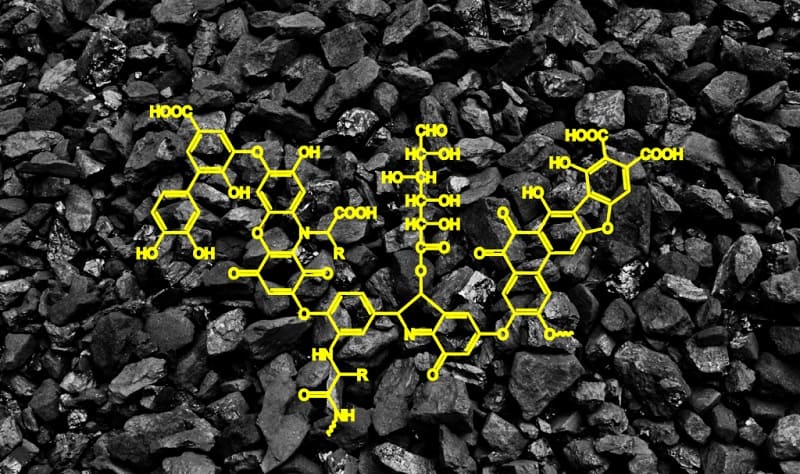
Differences between humic and fulvic acids
First, we explain what humic and fulvic acids are used for, what exactly the function of each one is.
Humic and fulvic acids are key organic components in agriculture.
Humic acids help improve soil structure and water retention, while fulvic acids promote nutrient uptake by plants and stimulate plant growth.
In these lines we quote the differences between humic and fulvic acids:
- Molecular size. Humic acids have a larger molecular size than fulvic acids.
- Solubility. Humics are less soluble in water.
- Origin and decomposition. Humic acids are formed from the decomposition of organic matter over a longer period, while fulvic acids are derived from more rapidly decomposing organic matter.
- Functions. Fulvic acids promote nutrient uptake by plants and stimulate plant growth, while humic acids primarily improve soil structure and retain nutrients.

Discover Fertiorgan Humus in Artal
This product stands out for its ability to significantly improve the physicochemical properties of the soil, composed of humic and fulvic acids derived from Leonardite.
It works by increasing microbial activity, which is crucial for soil health and plant growth. In addition, it improves the cation exchange capacity of the soil, allowing better assimilation of essential nutrients.
The guaranteed content of humic acids (8% w/w) and fulvic acids (7% w/w) in Fertiorgan Humus is notably beneficial, since these components favor the formation of complexes with mineral cations, improving the absorption of these nutrients by the plants.
This is especially useful in low organic matter soils, where the product acts to strengthen the clay-humic complex and improve the overall structure of the soil.
Its application is versatile and can be used in a wide variety of crops, including fruit, citrus, horticultural, extensive and ornamental crops, throughout the entire vegetative cycle.
This makes it an indispensable product for the integrated management of soil fertility in various agricultural systems.

The adjustable dosage of Fertiorgan Humus allows it to be adapted to the specific needs of each type of soil and phenological state of the crop, which maximizes the effectiveness of the product and helps achieve a more sustainable and productive agriculture.